SAMPLE LIKERT SCALE QUESTIONS
LI-CM-1
Context: Students have learned work and the relationship between work and energy. They are applying that knowledge to answer the following question:
"Consider a Daredevil Speedway with a number of loops and a ramp. A toy car can be wound several times. If the car is wound, there is a force pushing the car forward while it is in motion. But the force keeps changing. Consider a wound car started with a launcher. It has a mass of m. Its initial and final velocities are vi and vf. Its initial and final height are yi and yf. If friction is negligible, write an equation for the work done by the force pushing the car forward after it leaves the launcher."
You move to a table and notice that the students put on their white board the following equations:
Wnet = Wpush + Wgravity + Wnormal
Wnormal = 0
Wnet = 1⁄2mvf2 - 1⁄2mvi2
Wgravity = mgyf - mgyi
Wpush = Wnet - Wgravity = 1⁄2mvf2 - 1⁄2mvi2 - mgyf + mgyi
You ask the students to explain their answer to you. They say that “There are three forces in this case, gravity, push, and the normal force. The normal force does not do any work because it is always perpendicular to the motion. The work of the net force is the difference in kinetic energy. The work of the gravity is the difference in gravitational energy. When we plug them in, we get the work of the pushing force.”
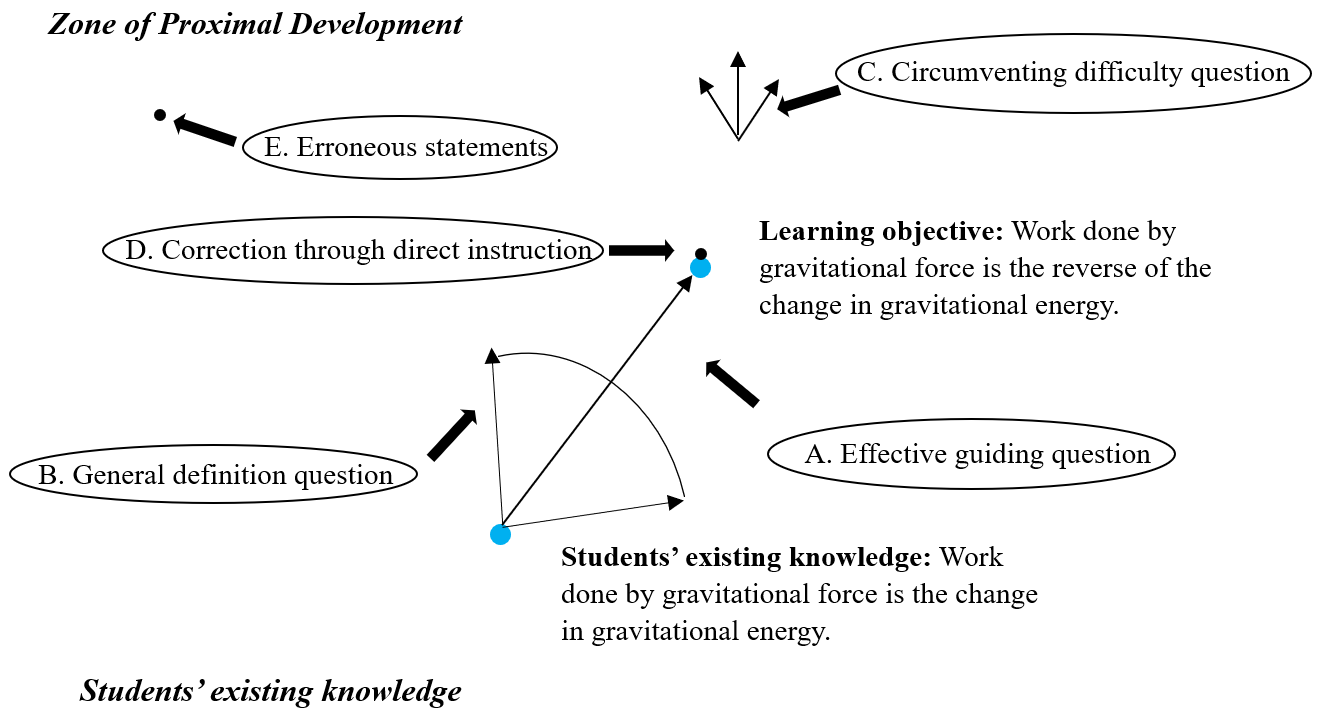
Your job as an LA is to identify students' needs or
difficulties and guide them to make a progress in their
learning. At this moment, how likely would you use the
responses below to continue the conversation with the
students? Indicate the likelihood of each response on a
five-point scale of 5(very likely), 4(likely), 3(Neutral),
2(unlikely), and 1(very unlikely).
A. If we drop a book, does the gravitational force on the
book do positive or negative work?
B. What is the formula of work? How does it apply to this problem?
C. What if the friction is not negligible? How would that change your equations?
D. Work done by the pushing force should be the change of mechanical energy.
E. Work done by the net force is not the change of kinetic energy.
Hypothetical impacts of Items A-E on students' learning