SAMPLE FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
FR-CM-1
Context: Students have learned work and the relationship between work and energy. They are applying that knowledge to answer the following question:
"Consider a Daredevil Speedway with a number of loops and a ramp. A toy car can be wound several times. If the car is wound, there is a force pushing the car forward while it is in motion. But the force keeps changing. Consider a wound car started with a launcher. It has a mass of m. Its initial and final velocities are vi and vf. Its initial and final height are yi and yf. If friction is negligible, write an equation for the work done by the force pushing the car forward after it leaves the launcher."
You move to a table and notice that the students put on their white board the following equations:
Wnet = Wpush + Wgravity + Wnormal
Wnormal = 0
Wnet = 1⁄2mvf2 - 1⁄2mvi2
Wgravity = mgyf - mgyi
Wpush = Wnet - Wgravity = 1⁄2mvf2 - 1⁄2mvi2 - mgyf + mgyi
You ask the students to explain their answer to you. They say that “There are three forces in this case, gravity, push, and the normal force. The normal force does not do any work because it is always perpendicular to the motion. The work of the net force is the difference in kinetic energy. The work of the gravity is the difference in gravitational energy. When we plug them in, we get the work of the pushing force.”
a. What can you conclude from the information provided about the students' content knowledge? What are the students' strengths and difficulties?
b. How would you respond to the students? Please use direct quotes of what you would say. What is the reasoning behind your response?
FR-CM-2
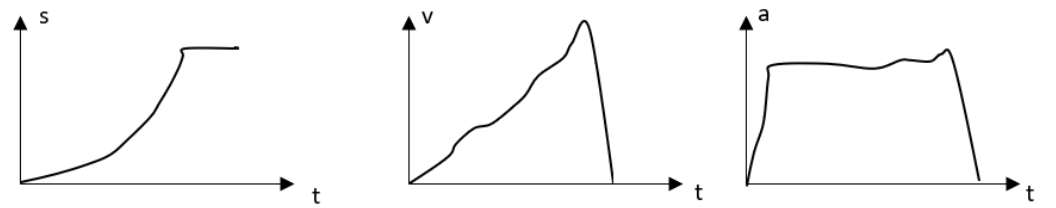
Context: A group of students are conducting a lab about free falling. They are required to use a motion detector to draw position vs. time (s-t),velocity vs. time (v-t), and acceleration vs. time (a-t) graphs of the free falling of three different objects, a book, a small basketball, and a box. The motion detector is held above the objects, facing downward. Moving away from the detector is recorded as the positive direction.
You approach this group to check whether the students understand the
relationship between s-t, v-t, and a-t graphs. Below is the
conversation you have with the students
You: What does the position graph tell you?
Student: It hit the ground and stopped.
You: OK. Does the velocity graph match the position graph?
Student: Yes, because it increases
You: OK. Does the acceleration graph match the velocity graph?
Student: Yes. If you are increasing at a constant rate, you cannot
accelerate. Right?
a. What can you conclude from the information provided about the students' content knowledge? What are the students' strengths and difficulties?
b. How would you respond to the students? Please use direct quotes of what you would say. What is the reasoning behind your response?
FR-EM-1
Context: Students have studied electric flux both qualitatively and quantitatively. They are qualitatively deriving Gauss's law
by drawing field lines through a closed surface.
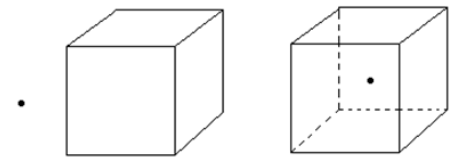
The students are given the following instructions: "Consider the illustrations shown below. Each picture contains one positive point charge and an imaginary box.
In each case, determine if there is net flux through the box. The total electric flux through the imaginary box is the sum of the electric flux through each surface of the box.
Remember that when the angle between the area vector of the surface and the direction of the electric field is greater than 90°, the flux is negative. What does the flux through the box depend on? When is there more net flux, less net flux, and zero net flux?"
You approach a group of students and have a conversation with them to check their understanding
You: Looking at the left picture, when the point charge is outside the box. What do the field lines look like?
Student: Radiate out from the positive charge.
You: OK, so what is the net flux?
Student: I think it's negative, because the left side of the box is closer to the point charge, so the flux into the box should be stronger than the flux out.
a. What can you conclude from the information provided about the students' content knowledge? What are the students' strengths and difficulties?
b. How would you respond to the students? Please use direct quotes of what you would say. What is the reasoning behind your response?
FR-EM-2
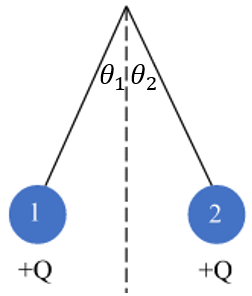
Context: Students are exploring the forces exerted by two identical charged pith balls on each other in different cases as shown in the figure below.